Japanese knotweed found to inhibit signaling, cell growth of hepatocellular carcinoma stem cells
06/14/2019 / By Evangelyn Rodriguez
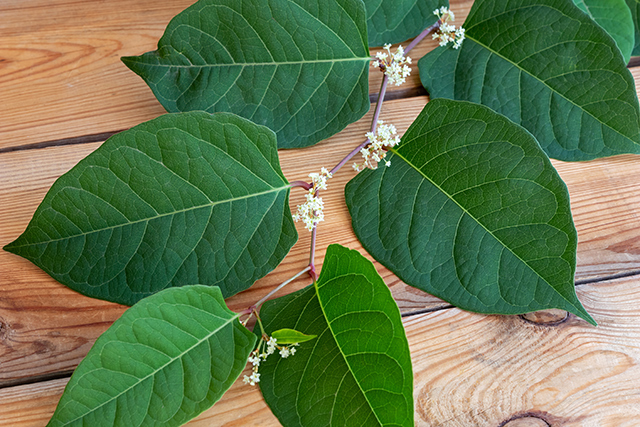

Researchers from Guangzhou University of Chinese Medicine in China isolated and identified small-molecule STAT3 signaling inhibitors from the root extracts of the Japanese knotweed (Polygonum cuspidatum). Their results, which included the evaluation of in vitro anticancer activities of these STAT3 signaling inhibitors, were published in the journal BMC Complementary and Alternative Medicine.
- STAT3 is an oncogene constitutively activated in hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) cells and HCC cancer stem cells (CSCs). It is a good target for HCC anticancer therapies.
- The researchers used various column chromatographies on silical gel, Sephadex LH-20, and preparative HPLC to isolate the components of the ethyl acetate extracts and subfractions of P. cuspidatum.
- They used NMR, MS, and IR analysis to determine the chemical structures of the components.
- To evaluate their inhibitory effects against STAT3, the researchers used a STAT 3-dependent luciferase reporter gene assay. They examined the tyrosine phosphorylation of STAT3 using Western Blot analysis.
- They used MTT assay, tumorsphere formation assay, and flow cytometry analysis to evaluate the effects of the STAT3 pathway inhibitors on the growth of human HCC cells, the self-renewal capacity of HCC CSCs, and their cell cycle and apoptosis, respectively.
- The researchers successfully isolated a novel juglone analog 2-ethoxystypandrone, along with seven other compounds.
- They found 2-ethoxystypandrone to be a novel and potent STAT3 signaling inhibitor; it inhibited the interleukin 6 (IL-6)-induced and constitutive activation of STAT3 in HCC cells.
- 2-ethoxystypandrone inhibited the survival of HCC cells, blocked tumorspheres formation, and induced apoptosis of HCC CSCs in a dose-dependent manner.
Based on these findings, the researchers concluded that 2-ethoxystypandrone is a potent STAT3 signaling inhibitor capable of inhibiting the proliferation of HCC cells and HCC CSCs, which makes it a promising anti-CSC agent.
Read the full study at this link.
Journal Reference:
Li W, Zhang Q, Chen K, Sima Z, Liu J, Yu Q, Liu J. 2-ETHOXYSTYPANDRONE, A NOVEL SMALL-MOLECULE STAT3 SIGNALING INHIBITOR FROM POLYGONUM CUSPIDATUM, INHIBITS CELL GROWTH AND INDUCES APOPTOSIS OF HCC CELLS AND HCC CANCER STEM CELLS. BMC Complementary and Alternative Medicine. February 2019;19(1). DOI: 10.1186/s12906-019-2440-9
Tagged Under: 2-ethoxystypandrone, alternative medicine, anticancer, apoptosis, cancer cures, cancer treatment, disease treatments, hepatocellular carcinoma, herbal medicine, Herbs, Japanese knotweed, liver health, longevity, natural cures, natural medicine, Polygonum cuspidatum, remedies, research, TCM, traditional Chinese medicine
RECENT NEWS & ARTICLES
PlantMedicine.News is a fact-based public education website published by Plant Medicine News Features, LLC.
All content copyright © 2018 by Plant Medicine News Features, LLC.
Contact Us with Tips or Corrections
All trademarks, registered trademarks and servicemarks mentioned on this site are the property of their respective owners.