Herbal mixture shown to alleviate inflammatory skin disorders
04/23/2019 / By Evangelyn Rodriguez
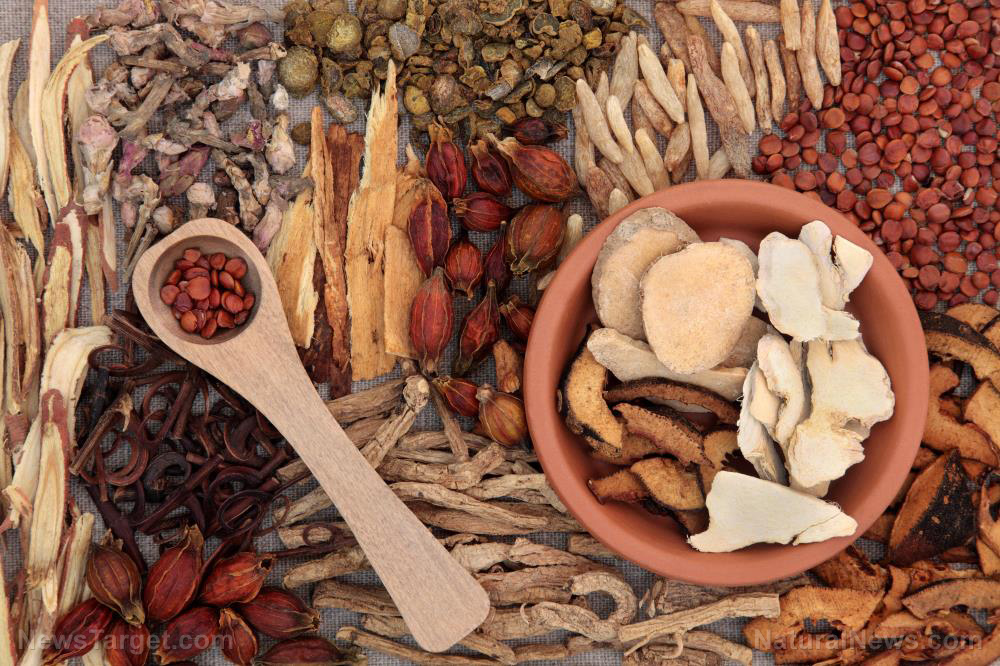

In this study, researchers from Kyungpook National University in South Korea evaluated the ability of a combination of five different plants to prevent atopic dermatitis (AD) in vivo and in vitro. The results of their study were published in the journal BMC Complementary and Alternative Medicine.
- The researchers used Cornus officinalis (Japanese cornelian cherry), Rosa multiflora (multiflora rose), Lespedeza bicolor (shrubby bushclover), Platycladus orientalis (Chinese thuja), and Castanea crenata (Korean chestnut) – all traditionally used to alleviate inflammatory skin disorders – to make an herbal mixture (C2RLP) against AD.
- They used murine, rat, and human cells to evaluate its effects in vitro.
- For in vivo studies, they purchased five-week-old, specific-pathogen-free male BALB/C mice.
- They measured nitric oxide (NO) and PGE2 (prostaglandin E2) production in vitro using a spectrophotometer and ELISA (enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay), respectively.
- They also evaluated the effect of C2RLP on iNOS (inducible nitric oxide synthase)-mRNA expression and TARC (thymus and activation-regulated chemokine) production, as well as the release of beta-hexosaminidase in vitro.
- The researchers also tested C2RLP for antioxidant activity and used liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry (LC-MS) to identify the active compounds present in it.
- For in vivo studies, they tested the toxicity of C2RLP on Sprague-Dawley rats; BALB/C mice were used for the rest of the experiment.
- They induced lesions on the mice and treated them with an ointment made from C2RLP for 25 days; a histopathological examination was done to determine the degree of hyperplasia (tissue enlargement), inflammation and mast cell infiltration.
- The levels of cytokines such as IL-2, IL-4, IL-5, IL-6, IL-13 and IFN-gamma were determined from blood samples. Cytokines are signaling molecules secreted by immune cells that promote inflammation.
- C2RLP was able to reduce AD and suppress histopathological changes in the mice. It also reduced IL-4 levels in the blood, as well as the production of NO, PGE2, and TARC.
- C2RLP, at high concentrations, also inhibited iNOS-mRNA expression in vitro and beta-hexosaminidase release. Furthermore, it exhibited antioxidant activity against the free radical DPPH.
- LC-MS analysis revealed the presence of compounds like loganin (anti-inflammatory), ellagic acid (anti-cancer), and kaempferol 3 glucoside (anti-inflammatory) in C2RLP.
Based on their results, the researchers concluded that the herbal mixture C2RLP has the ability to protect against AD by down-regulating immune responses and suppressing inflammatory mediators.
Read the whole study at this link.
Journal Reference:
Mechesso AF, Lee SJ, Park NH, Kim JY, Im ZE, Suh J-W, Park S-C. PREVENTIVE EFFECTS OF A NOVEL HERBAL MIXTURE ON ATOPIC DERMATITIS-LIKE SKIN LESIONS IN BALB/C MICE. BMC Complementary and Alternative Medicine. 18 January 2019;19(1). DOI: 10.1186/s12906-018-2426-z
Tagged Under: alternative medicine, antioxidant, Chinese thuja, cytokines, disease treatments, Ellagic acid, herbal medicine, herbal mixture, Herbs, inflammation, Interleukin, Japanese cornelian cherry, kaempferol, Korean chestnut, loganin, multiflora rose, natural cures, natural medicine, nitric oxide, phytochemicals, prostaglandin, remedies, research, shrubby bushclover