Compounds in foxtail found to show potential in treating toothache and heartburn
10/25/2018 / By Ellaine Castillo

Plants are an invaluable part of disease treatment and management, especially in developing countries. These plants contain bioactive compounds that are responsible for their different medicinal properties. In order to maximize a plant’s potential use for medicinal purposes, it is crucial to determine the phytochemicals involved in its therapeutic activities. This is what researchers from Brazil aimed to do when they conducted a phytochemical and antimicrobial analysis of extracts derived from foxtail (Harrisia adscendens) roots, which are used in traditional medicine.
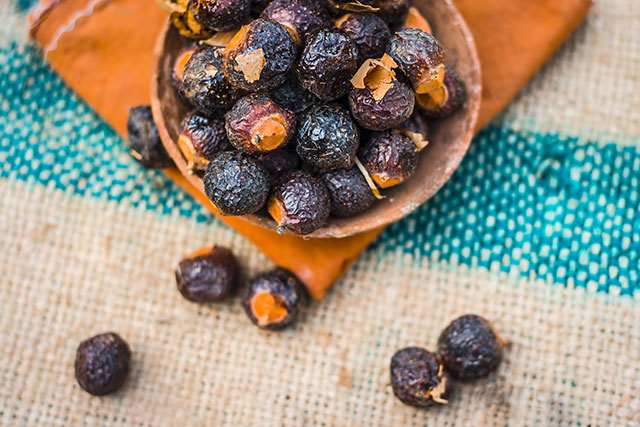
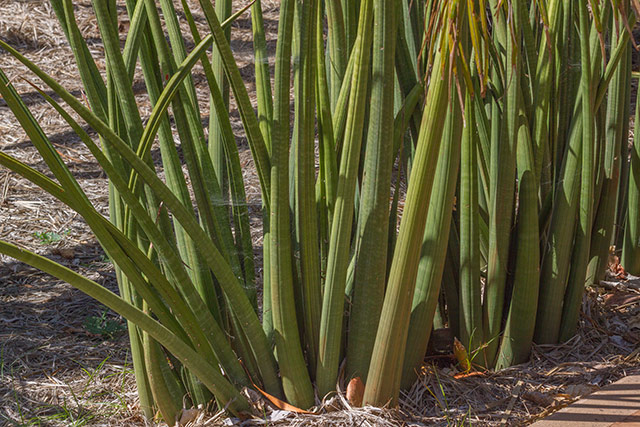
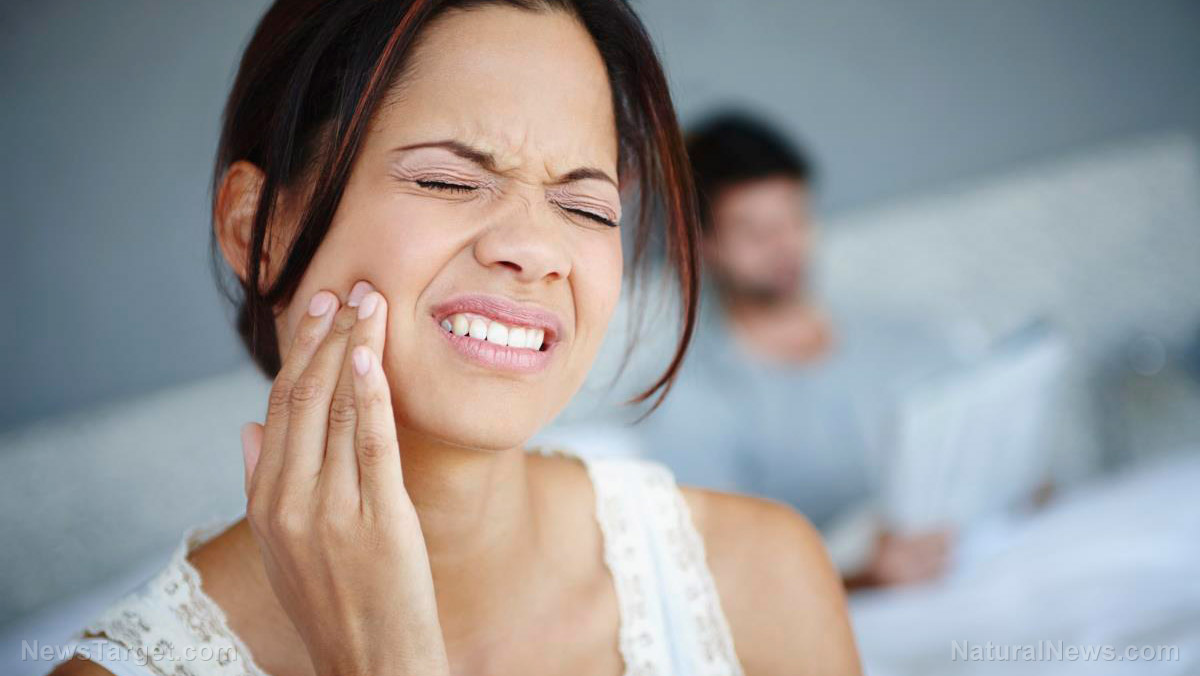
Foxtail is a species of cactus native to the savanna. It is traditionally used for treating burning sensations like heartburn, kidney problems, and toothaches. These conditions are known to have pain as one of their symptoms. Although foxtail roots are commonly used for such ailments, the compounds involved in the alleviation of these conditions have not been determined prior to this study.
In this study, which was published in the Brazilian Journal of Pharmacognosy, the researchers determined the phytochemicals present in foxtail root extracts through chromatography and spectroscopy. Results of these experiments showed that the main components of foxtail extracts are the alkaloid beta-carboline and an acetophenone. The presence of beta-carboline was attributed to foxtail’s ability to relieve pain, which is how this compound works in the central nervous system. Previous studies have shown that beta-carboline has relaxant, anticonvulsant, antitumor, and antimicrobial properties, which means that foxtail can also be used for these effects.
Aside from phytochemical analysis, the researchers also determined the antimicrobial activity of foxtail extracts. They were able to determine that the extracts were active against Pseudomonas aeruginosa, which is promising since this pathogen is the leading cause of most infections. Additionally, P. aeruginosa exhibits inherent resistance against many antimicrobial compounds so the discovery of potential treatments against it is crucial.
From these results, it can be determined that foxtail extracts contain compounds, namely acetophenone and beta-carboline, which can be attributed to the plant’s ability to remedy pain associated with toothaches and heartburn. With further validation, foxtail could be developed into a safe and effective alternative for prescription drugs. (Related: Heartburn is a symptom – and meds are NOT the solution: Prescriptions for heartburn DOUBLE your risk of stomach cancer.)
Natural remedies for toothaches
Aside from foxtail, there are other remedies for toothaches. These include the following:
- Salt water rinse – Rinsing the mouth with salt water helps remove food stuck in the crevices of the teeth. Aside from this, salt water also kills microbes that cause infections and reduces inflammation. It is very easy to make a salt water rinse. Just add half a teaspoon of salt to a glass of warm water and it’s ready good for use.
- Cold compress – Applying a cold compress is a common way of alleviating pain and reducing inflammation. This method is especially useful for toothaches caused by external forces. Do this by putting the cold compress on the affected area and leaving it on for 20 minutes.
- Garlic – Eating garlic is associated with many health benefits. These include antibacterial activity, which is useful for preventing plaques that could cause tooth decay. Aside from this, garlic can also alleviate pain. There are two ways to use garlic for treating toothaches. One of these is by turning it into a paste while the other is simply chewing a clove of garlic.
- Peppermint – Putting a slightly warm peppermint tea bag over the affected area can help numb the pain and prevent sensitive gums.
Learn more about the potential uses of foxtail and other herbs by visiting Cures.news today.
Sources include:
Tagged Under: acetophenone, alkaloids, beta-carboline, Cactus, foxtail, Harrisia adscendens, heartburn, herbal medicine, natural remedies, oral health, pain relief, phytochemical analysis, phytochemicals, research, secondary metabolites, toothache, traditional medicine