Peppermint shows potential for killing drug-resistant bacteria
10/21/2018 / By Michelle Simmons
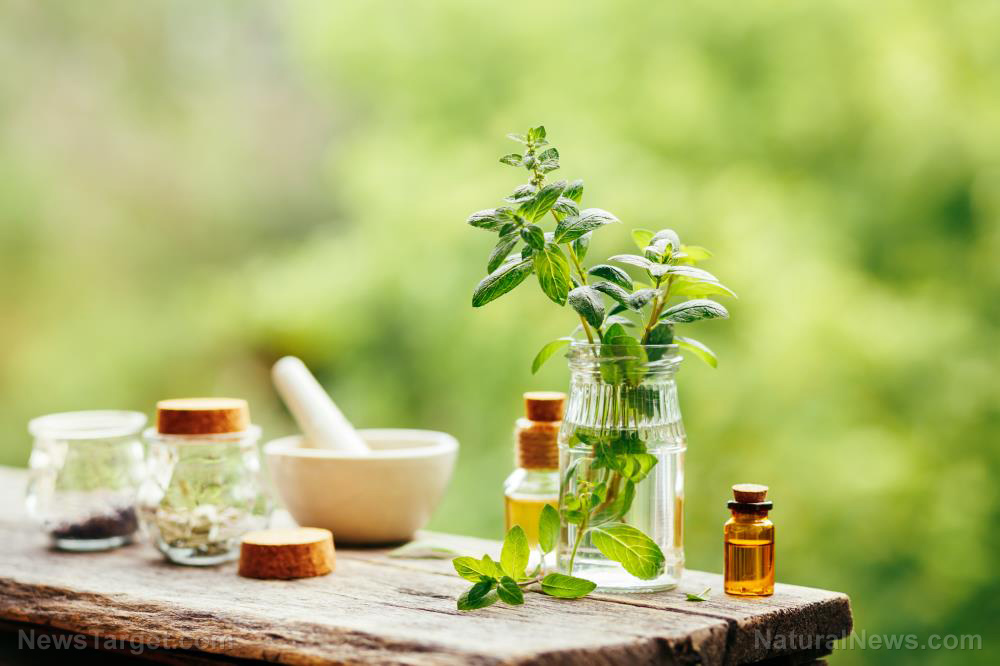

Many plants have great potential in treating infectious diseases, especially drug-resistant ones. One of these plants is peppermint (Mentha piperita). Researchers from Najran University in Saudi Arabia have found that peppermint has potent antibacterial activity, making it a great potential antibacterial agent against many multi-drug resistant pathogens.
In the study, which was published in the Journal of Herbal Medicine, the researchers evaluated the antimicrobial and antibacterial activities of peppermint against several pathogens. They used different forms of peppermint extracts: ethanol, methanol, ethyl acetate, and chloroform.
They tested these peppermint extracts against several multi-drug resistant pathogenic bacterial clinical isolates, including Streptococcus pyogenes, Staphylococcus epidermidis, Enterococcus faecalis, S. aureus, E. coli, Klebsiella pneumonia, Acinetobacter baumannii, and Stenotrophomonas maltophilia.
In order to evaluate the antibacterial activities of these peppermint extracts, the researchers used the standard minimal inhibitory concentration (MIC) and minimal bactericidal concentration (MBC) methods.
Based on the results of the study, the ethyl acetate peppermint extract exhibited the most potent inhibitory effect, particularly inhibiting the growth of all the tested pathogens. The chloroform, ethanol, and methanol peppermint extracts followed.
The results also revealed that S. pyogenes had the lowest MIC value, which means that its growth can be inhibited with the lowest concentration of the peppermint extract. Methicillin-resistant S. epidermidis and E. faecalis came after S. pyogenes. On the other hand, the MBC values of all extracts were higher than the corresponding MIC for most of the pathogens.
The findings of the study demonstrated that peppermint has potent antibacterial potential against multi-drug resistant pathogens S. pyogenes, E. faecalis, S. aureus, S. epidermidis, E. coli, and Klebsiella pneumonia.
Overall, the researchers concluded that peppermint can potentially be used as an antibacterial agent against many multi-drug resistant pathogens. (Related: Drug-resistant bacteria increasingly common in US hospitals.)
Peppermint and its other uses
Peppermint is an aromatic plant that is a hybrid of watermint and spearmint. It is available in the form of leaves, capsules, and oil. Its leaves, fresh or dry, can be used in food to add flavor or fragrance. Its leaves are used to make tea. Its essential oil is used in cosmetics, soaps, toothpaste, mouthwashes, and other products. Peppermint has also been used as a popular traditional remedy for various health conditions. These include the following:
- Colds and flu: Peppermint contains menthol, which is an effective decongestant that can reduce the swelling membranes in the nose. In addition, peppermint is an expectorant, which means that it can loosen and remove mucus from the lungs.
- Headaches and migraines: Peppermint oil can help ease headaches and migraines because of its relaxing effect. To relieve a headache, apply diluted peppermint oil on your forehead.
- Healing wounds: Peppermint can be used to heal wounds. The antibacterial compounds from peppermint can also help kill bacteria and promote wound healing.
- Indigestion: Peppermint is believed to have calming effects. It is an ideal treatment for indigestion because it can calm the stomach muscles and improve the flow of bile, according to the University of Maryland Medical Center (UMM).
- Irritable bowel syndrome (IBS): Many studies have also suggested that various forms of peppermint can help treat the symptoms of IBS, including pain, bloating, diarrhea, and gas.
- Nausea and vomiting: Studies have also shown that peppermint oil is a safe and effective treatment for relieving nausea and vomiting.
- Skin problems: Peppermint essential oil is commonly used to relieve skin irritation and itchiness, and to reduce redness. Just remember that peppermint essential oil should always be diluted first before applying to the skin. Mix three to five drops of peppermint essential oil with an ounce of a carrier oil like mineral or olive oil. Also, remember to test a small amount on the forearm to avoid an allergic reaction.
Read more news stories and studies on natural ways to fight drug-resistant bacteria by going to SuperBugs.news.
Sources include:
Tagged Under: alternative medicine, antibacterial, Antimicrobial, antimicrobial resistance, bacteria, essential oils, herbal medicine, Herbs, Mentha piperita, multi-drug resistant, multi-drug resistant bacteria, multidrug resistant pathogens, natural antibiotics, natural cures, natural healing, natural medicine, natural remedies, peppermint, superbugs