Evaluating the cardioprotective and antiarrhythmic effects of the Nardostachys chinensis
09/28/2018 / By RJ Jhonson
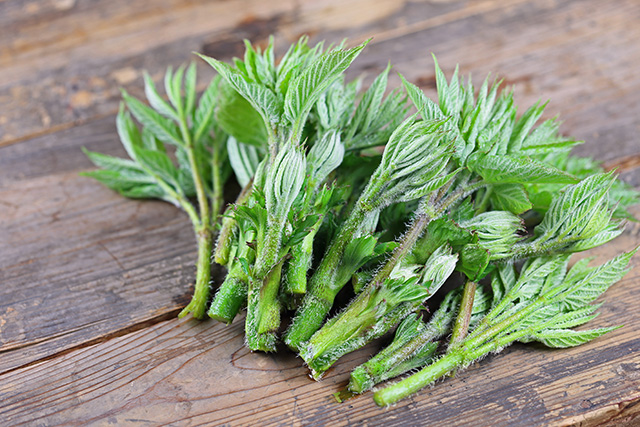

The spikenard or Nardostachys chinensis (NC) has been associated in previous studies with proper heart health and rhythm. A study published in BMC Complementary and Alternative Medicine compiled past literature on NC to present evidence of the herb’s cardioprotective and antiarrhythmic qualities.
- The spikenard has been valued in Chinese medicine for its ability to restore balance to the qi or the body’s life force. It is also used to treat a variety of conditions, such as indigestion, epilepsy, hysteria, and others.
- The authors identified studies on NC by using five databases: PubMed, The Cochrane Library, China National Knowledge Infrastructure (CNKI), the Wanfang Database, and the Chinese Scientific Journal Database (VIP).
- To find related studies, they used a set of general terms: “Nardostachys chinensis,” “Nardostachys chinensis Batal,” “Nardostachys jatamansi DC,” “Nardosinone,” “Nardostahyos Radix et Rhizoma,” “Animal,” “Mouse,” “Mice,” “Rat,” “Rabbit,” “Pig,” “Swine,” “Hog,” “Sheep,” “Dog,” “Monkey,” “Cat,” “Ape,” “Hominoidea,” and “cell.”
- Their review included only those papers that discussed the cardiovascular system in either animal or cell experiments that used NC (or its active compounds) as medicine. Studies that used proprietary Chinese medicine or traditional Chinese recipes were excluded, even when said treatments used NC as their main ingredient.
- They identified 16 studies, 11 of which were cell experiments and five were animal experiments. Four of the studies discussed NC’s ability to protect the myocardium from oxidative stress, inflammation, and apoptosis. Additionally, 12 of the studies touted the benefits of NC in preventing arrhythmia by regulating ion channels.
The researchers concluded that the findings demonstrated evidence of NC’s antiarrhythmic and cardioprotective benefits, but warned that the results could be interpreted another way because of the deficiencies and limitations of the studies cited.
Read the full text of the study at this link.
Journal Reference:
Li M, Xu X, Yang X, Kwong JSW, Shang H. THE CARDIOPROTECTIVE AND ANTIARRHYTHMIC EFFECTS OF NARDOSTACHYS CHINENSIS IN ANIMAL AND CELL EXPERIMENTS. BMC Complementary and Alternative Medicine. 2017;17(1). DOI: 10.1186/s12906-017-1910-1
Tagged Under: alternative medicine, arrhythmia, Bradycardia, cardiovascular health, Chinese medicine, food as medicine, food cures, heart disease, heart health, herbal medicine, Nardostachys chinensis, science, spikenard, tachycardia