Food for your skin: Use marula to prevent wrinkles and keep your skin baby soft
07/16/2018 / By Michelle Simmons

Wrinkles and skin aging can be prevented naturally with the plant called marula (Sclerocarya birrea [A. Rich.] Hochst), according to a study published in the journal BMC Complementary and Alternative Medicine. In the study, researchers in South Africa looked at the collagenase and elastase inhibition activity of extracts of the marula plant.
Natural compounds from plants have been shown to prevent elastase and collagenase activity and promote elastin and collagen activity. Elastin is the protein responsible for skin elasticity, while collagen is responsible for both the strength and elasticity of the skin. When elastin and collagen are broken down by elastase and collagenase, respectively, skin ages and wrinkles begin to form.
For the study, the researchers collected the extracts of marula from its stems, leaves, and fruits. They used acetone, ethanol, and methanol to create different marula extract concentrations. Marula oil, which is used in cosmetics, was also assessed in the study. The researchers then identified the active compound in the marula extracts by using pure standards and assessed their collagenase and elastase inhibition activity.
Researchers observed that the extracts from marula stem exhibited the most promising activity against elastase and collagenase. Meanwhile, the leaf extract exhibited moderate anti-elastase activity, while marula fruit extract and marula oil displayed limited inhibition activities against the two enzymes.
Out of the three concentrations of marula extracts used in the study, ethanolic extract of marula stems was revealed to be the most suitable because of its acceptability to be used for skincare and its inhibitory effect against collagenase activity. Moreover, defatting and concentration enhanced its anti-aging activity and reduced the intensity of the color of the extracts.
They also found that the main compounds of the ethanolic marula stems were quinic acid, catechin, epigallocatechin gallate, and epicatechin gallate. The epigallocatechin gallate and epicatechin gallate were revealed to be contributing to the anti-aging activity of marula.
The findings of the study suggest that the ethanolic extract of marula stems can inhibit elastase and collagenase activity, which in turn prevent the formation of wrinkles and skin aging.
Other natural anti-aging treatments
There are other natural ways to prevent skin aging. Here are three natural ingredients that can help keep the skin healthy:
- Aloe vera – Aloe vera is packed with vitamins, minerals, amino acids, fatty acids, and water. Because of its high water content, it serves as a great skin moisturizer. Moreover, aloe vera has been found to increase skin elasticity. It also contains malic acid, which can help reduce wrinkles, and zinc, which makes pores smaller and improves collagen formation. Aloe vera’s leaf pulp is also rich in fiber and nutrients that benefit the inside of the body. Ingesting aloe vera as a drink can soothe the lining of the digestive tract, reduce inflammation, enhance the repair of ulcers in the stomach and intestines, and help the immune system remove toxins with its antiviral, antibacterial, and anti-fungal properties. This detoxifies the body, which in turn slows down aging.
- Coconut oil – Coconut oil is not just for cooking, but also for taking care of the skin. It helps lessen wrinkles and fine lines by strengthening connective tissues and exfoliating the epidermis or the outermost layer of the skin. It also contains potent antioxidants and vitamins A and E, which are important for collagen production.
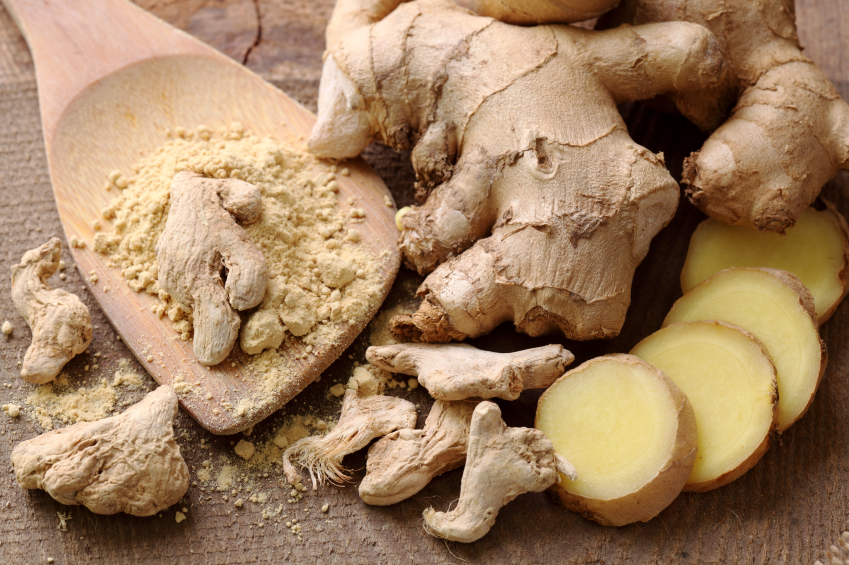
- Ginger tea – Drinking ginger tea can protect collagen and lessen skin damage and inflammation because of the vegetable’s antioxidant properties. You can make tea by shredding ginger and combining it with honey in hot water. (Related: Top 10 anti-aging foods.)
Read more news stories and studies on preventing skin aging by going to Cosmetics.news.
Sources include:
Tagged Under: anti-aging, anti-collagenase, anti-elastase, collagen, collagenase, elastase, food is medicine, marula, marula extracts, natural cures, natural remedies, Natural Treatments, science, Sclerocarya birrea, skin aging, skin aging prevention, skin health